Swiss Policy Research | Updated: December 2021
Fully referenced facts about covid-19, provided by experts in the field, to help our readers make a realistic risk assessment.
“The only means to fight the plague is honesty.” (Albert Camus, 1947)
Overview
- Lethality: According to the latest immunological studies, the overall infection fatality rate (IFR) of covid in the general population is about 0.1% to 0.5% in most countries, which is most closely comparable to the medium influenza pandemics of 1936, 1957 and 1968.
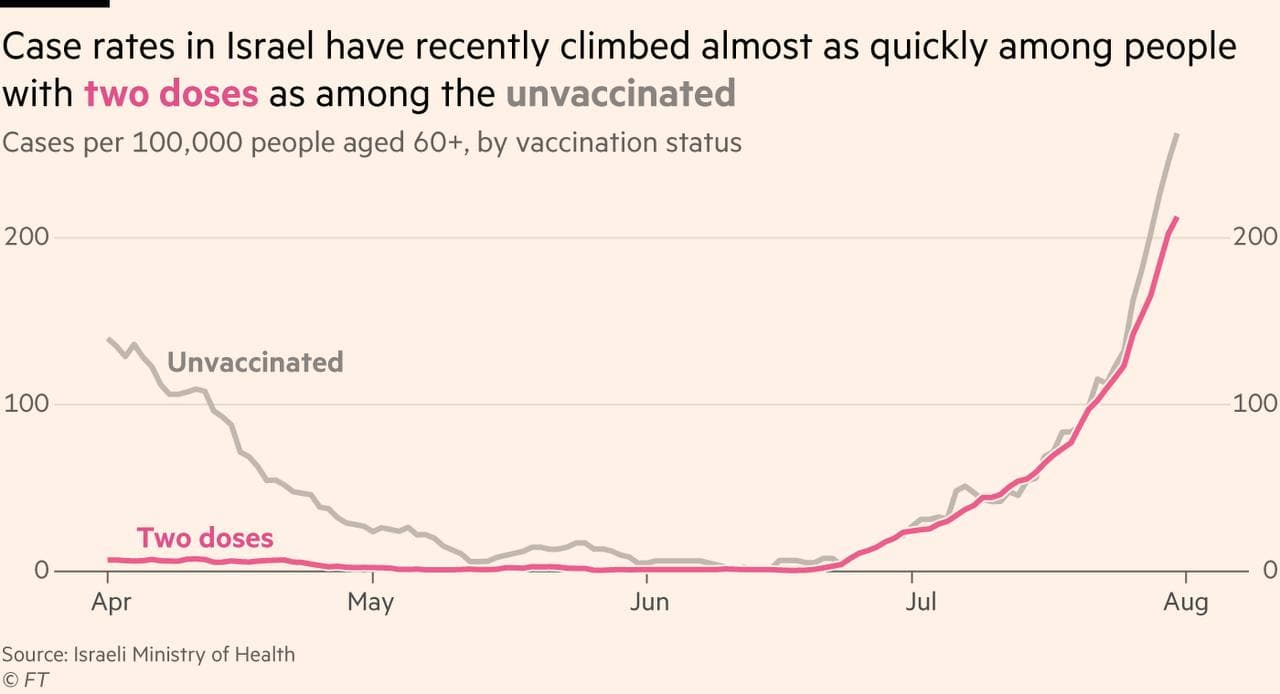
- Vaccines: Real-world studies have shown a very high, but rapidly declining covid vaccine effectiveness against severe disease. Vaccination cannot prevent infection and transmission. Various severe and fatal vaccine adverse events have been reported, including in young people. A prior infection generally confers superior immunity compared to vaccination.
- Treatment: For people at high risk or high exposure, early or prophylactic treatment is essential to prevent progression of the disease. According to numerous international studies, early outpatient treatment of covid may significantly reduce hospitalizations and deaths.
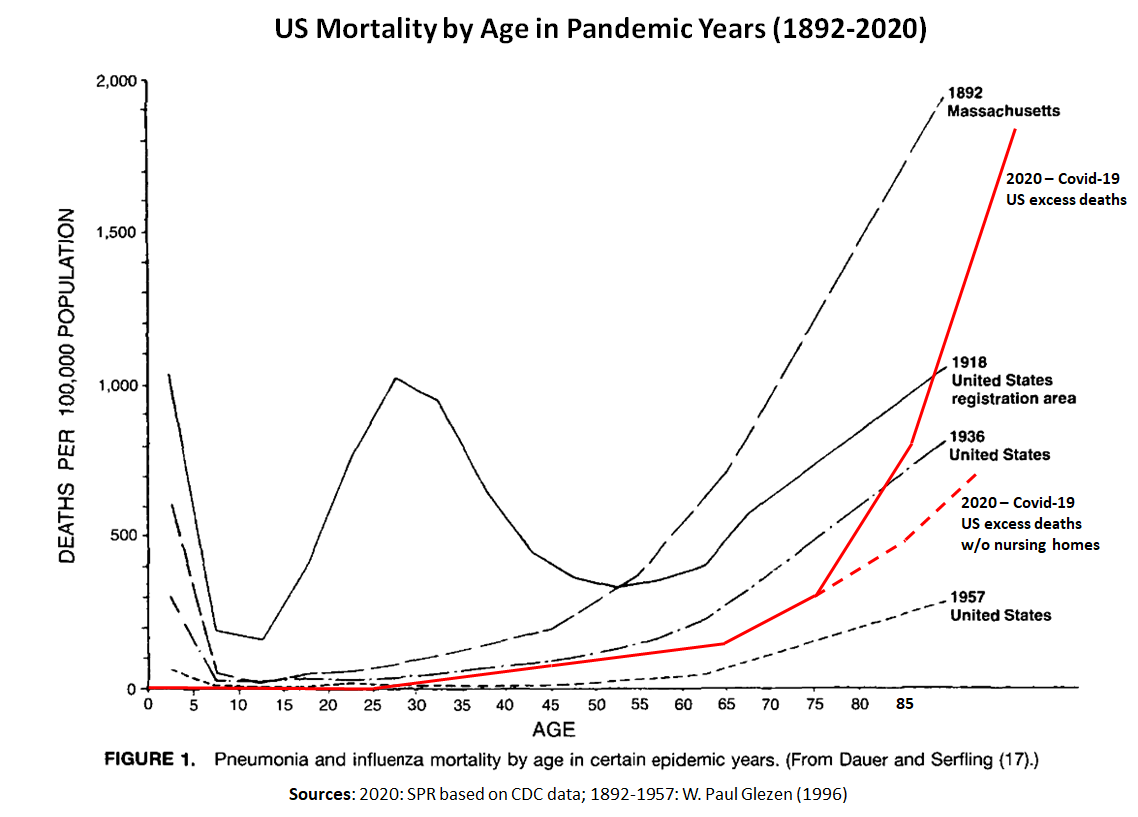
- Age profile: The median age of covid deaths is over 80 years in most Western countries (78 in the US) and about 5% of the deceased had no serious preconditions. The age and risk profile of covid mortality is therefore comparable to normal mortality, but increases it proportionally.
- Nursing homes: In many Western countries, about 50% of all covid deaths have occurred in nursing homes, which require targeted and humane protection. In some cases, care home residents died not from the coronavirus, but from weeks of stress and isolation.
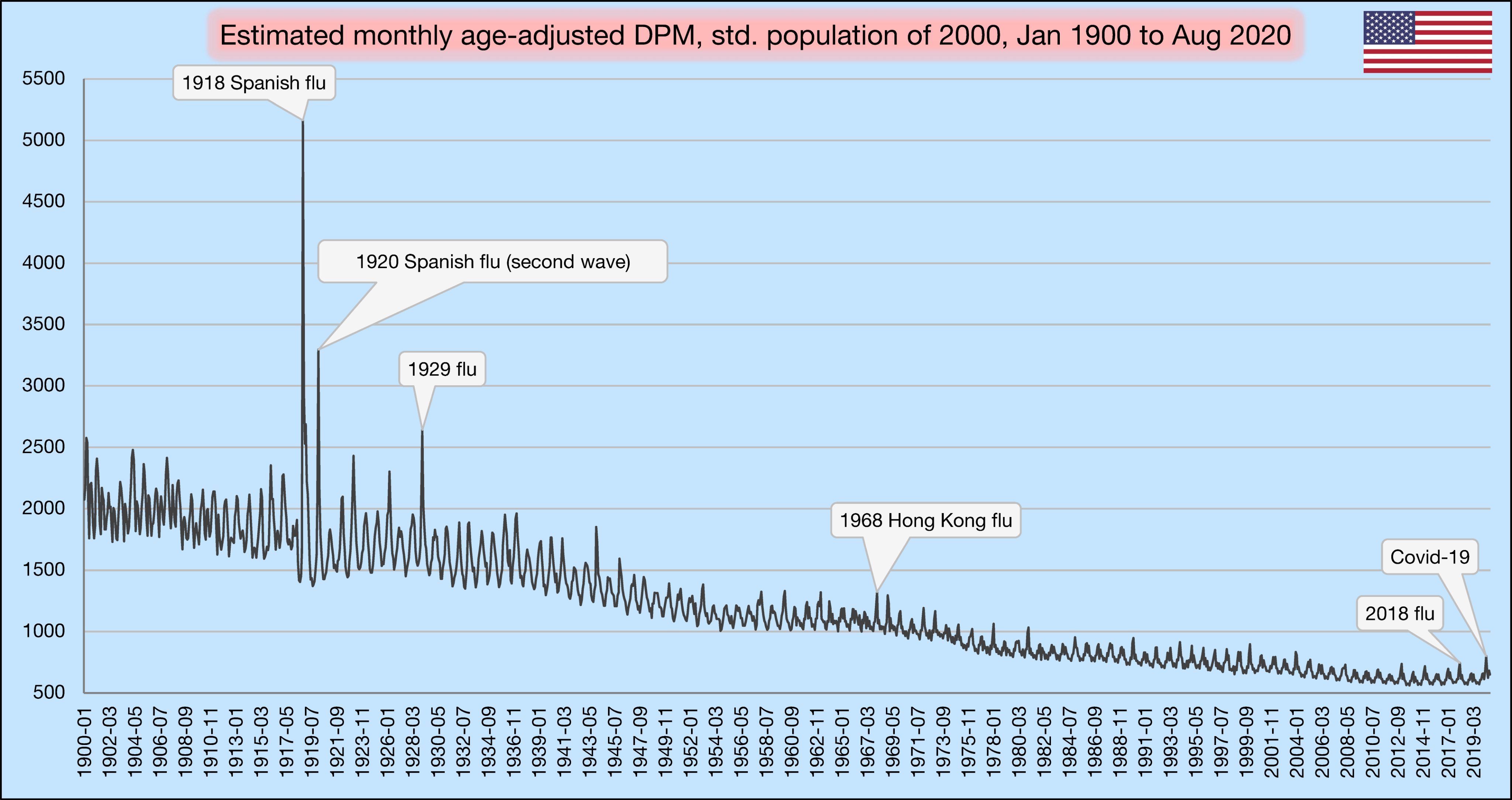
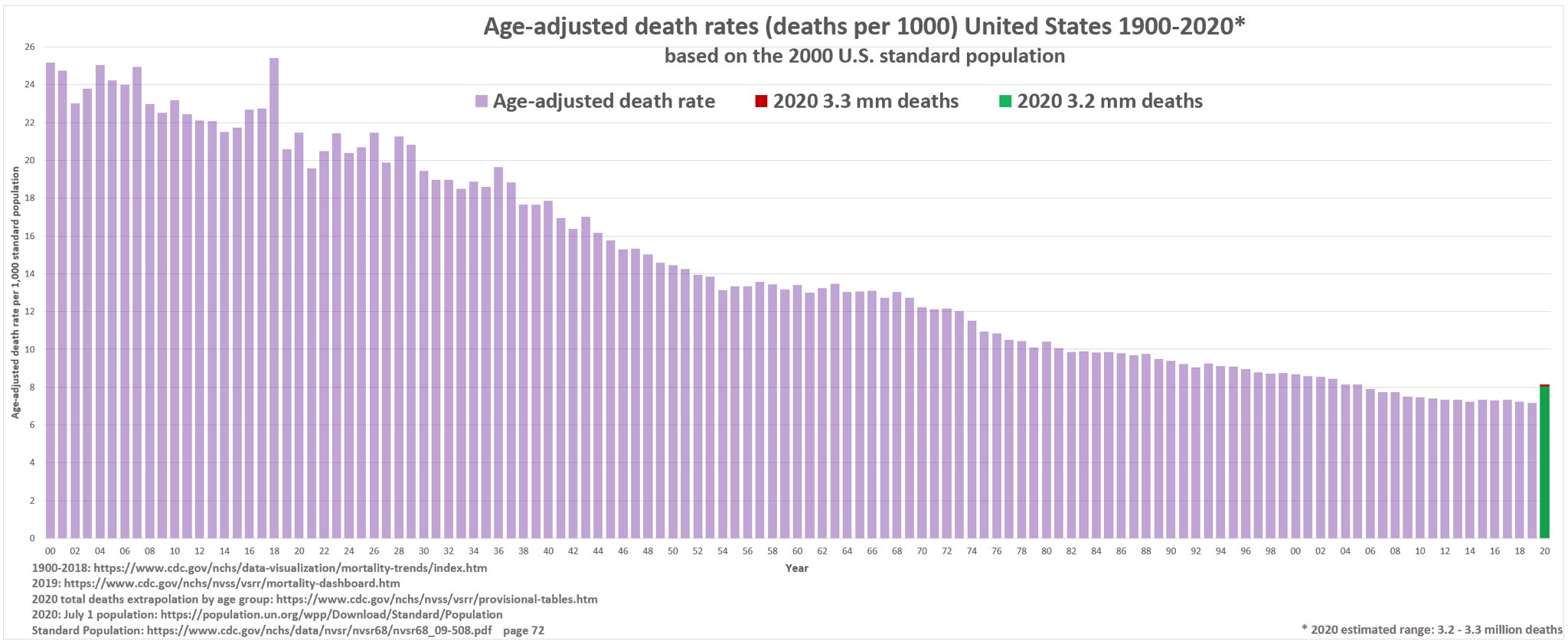
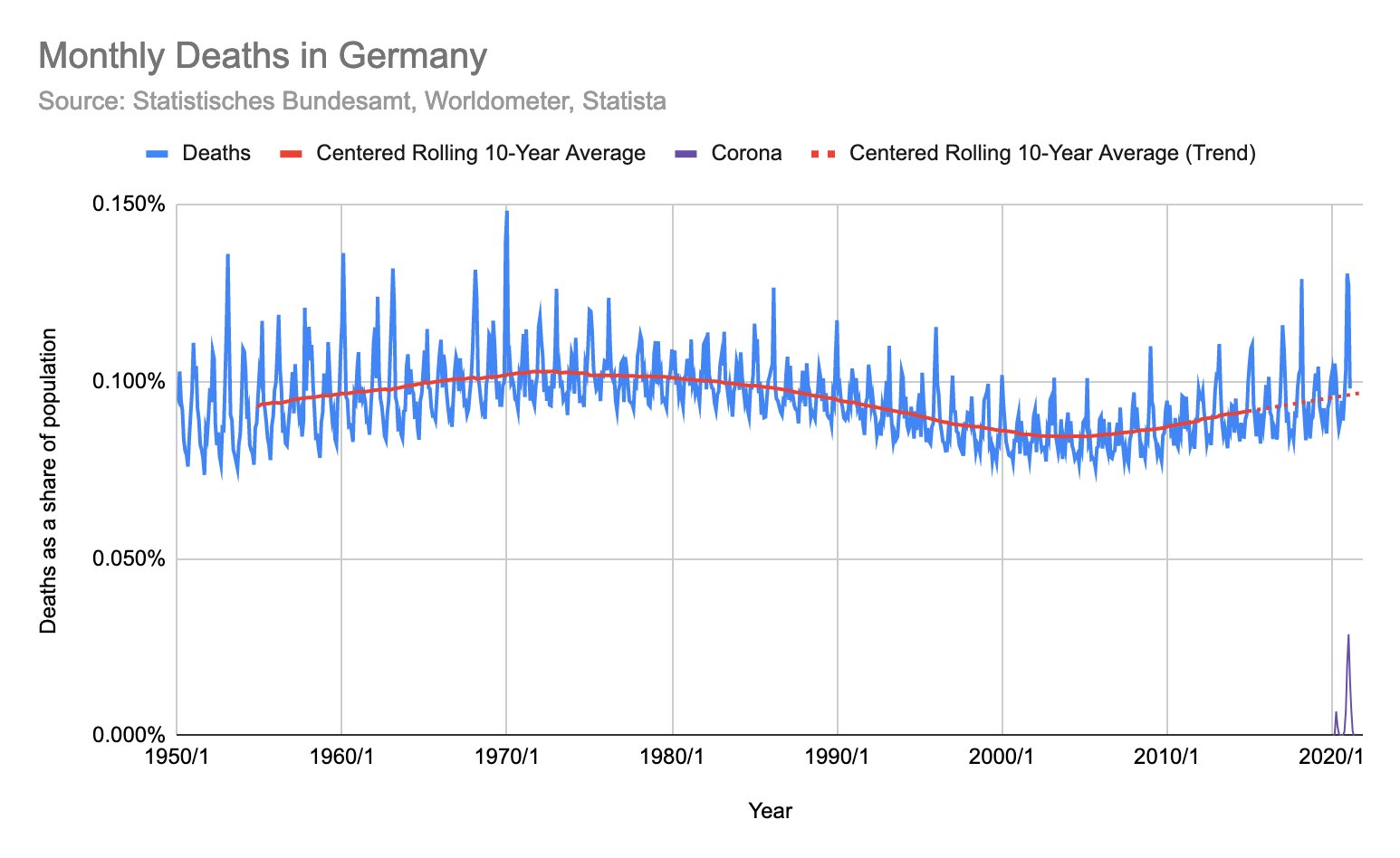
- Excess mortality: Overall, the pandemic has increased mortality by 5% to 25% in most Western countries. In some countries, up to 30% of additional deaths have been caused not by covid, but by indirect effects of the pandemic and lockdowns (including drug overdose deaths).
- Antibodies: By the end of 2020, between 10% and 30% of the population in most Western countries had coronavirus antibodies. In India and some Latin American countries, coronavirus infection prevalence reached up to 75% by the summer of 2021.
- Symptoms: About 30% of all infected persons show no symptoms. Overall, about 95% of all people develop at most mild or moderate symptoms and do not require hospitalization. Early outpatient treatment may significantly reduce hospitalizations.
- Long covid: Up to 10% of symptomatic people experience post-acute or long covid, i.e. covid-related symptoms that last several weeks or months. Long covid may also affect younger and previously healthy people whose initial course of disease was rather mild.
- Transmission: Indoor aerosols appear to be the main route of transmission of the coronavirus, while outdoor aerosols, droplets, as well as most object surfaces appear to play a minor role. The coronavirus season in the northern hemisphere usually lasts from November to April.
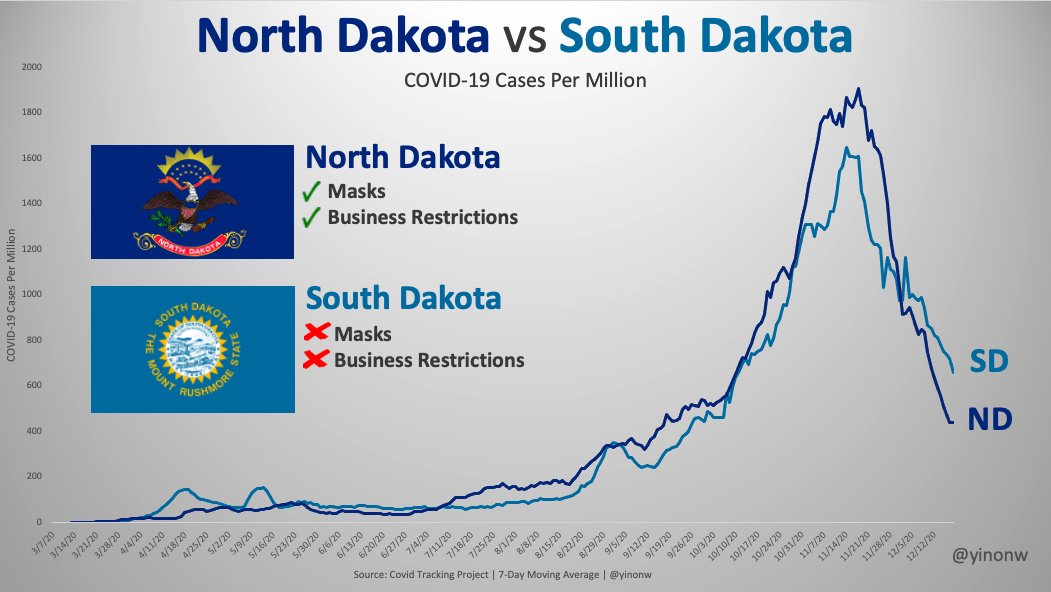
- Masks: There is still little to no scientific evidence for the effectiveness of face masks in the general population, and the introduction of mandatory masks couldn’t contain or slow the epidemic in most countries. If used improperly, masks may increase the risk of infection.
- Children and schools: In contrast to influenza, the risk of disease and transmission in children is rather low in the case of covid. There was and is therefore no medical reason for the closure of elementary schools or other measures specifically aimed at children.
- Contact tracing: A WHO study of 2019 on measures against influenza pandemics concluded that from a medical perspective, contact tracing is “not recommended in any circumstances”. Contact tracing apps on cell phones have also proven ineffective in most countries.
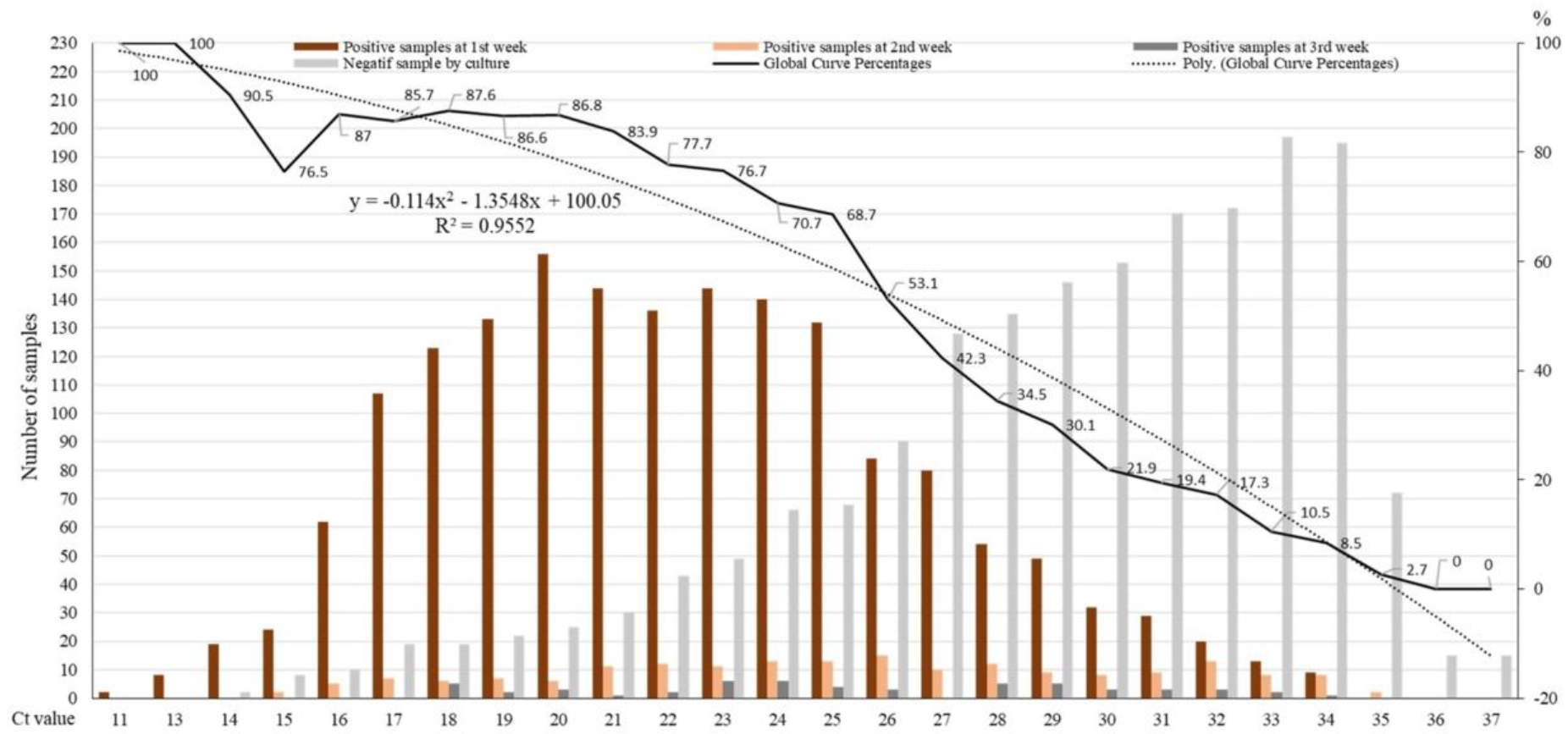
- PCR tests: The highly sensitive PCR test kits may in some cases produce false positive or false negative results or react to non-infectious virus fragments from a previous infection. In this regard, the so-called cycle threshold or ct value is an important parameter.
- Virus mutations: Similar to influenza viruses, mutations occur frequently in coronaviruses. Most of these mutations are insignificant, but some of them may increase the transmissibility, virulence or immune evasion of the virus to some extent.
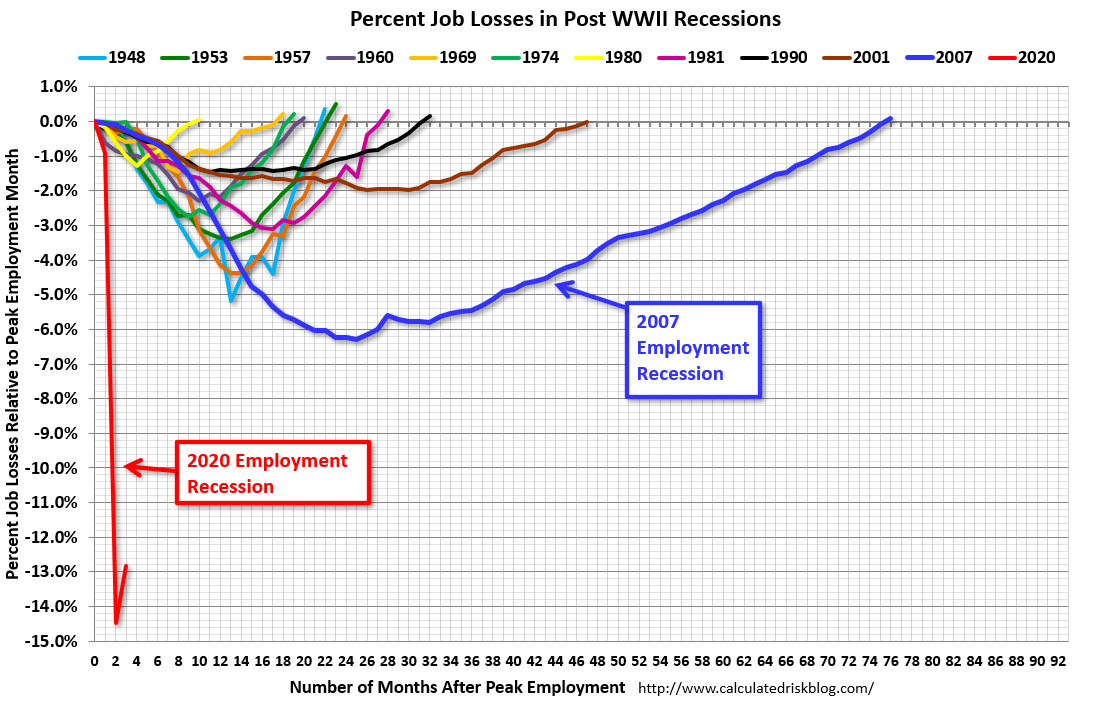
- Lockdowns: In contrast to early border controls, lockdowns have had no significant effect on the pandemic. According to the UN, lockdowns may put the livelihood of 1.6 billion people at acute risk and may push an additional 150 million children into poverty.
- Sweden: In Sweden, covid mortality without lockdown has been comparable to a strong influenza season and somewhat below the EU average. About 50% of Swedish deaths occurred in nursing homes and the median age of Swedish covid deaths was about 84 years.
- Media: The reporting of many media has been unprofessional, has increased fear and panic in the population and has led to a hundredfold overestimation of the lethality of the coronavirus. Some media even used manipulative pictures and videos to dramatize the situation.
- Virus origin: The origin of the new coronavirus remains unknown, but the best evidence currently points to a covid-like pneumonia incident in a Chinese mine in 2012, whose virus samples were collected, stored and researched by the Wuhan Institute of Virology (WIV). Due to cooperations, some US labs may also have had access to these viruses.
- Surveillance: NSA whistleblower Edward Snowden warned that the coronavirus pandemic may be used to expand global surveillance. Many governments have restricted fundamental rights of their citizens and announced plans to introduce digital biometric vaccine passports.
Overview diagrams






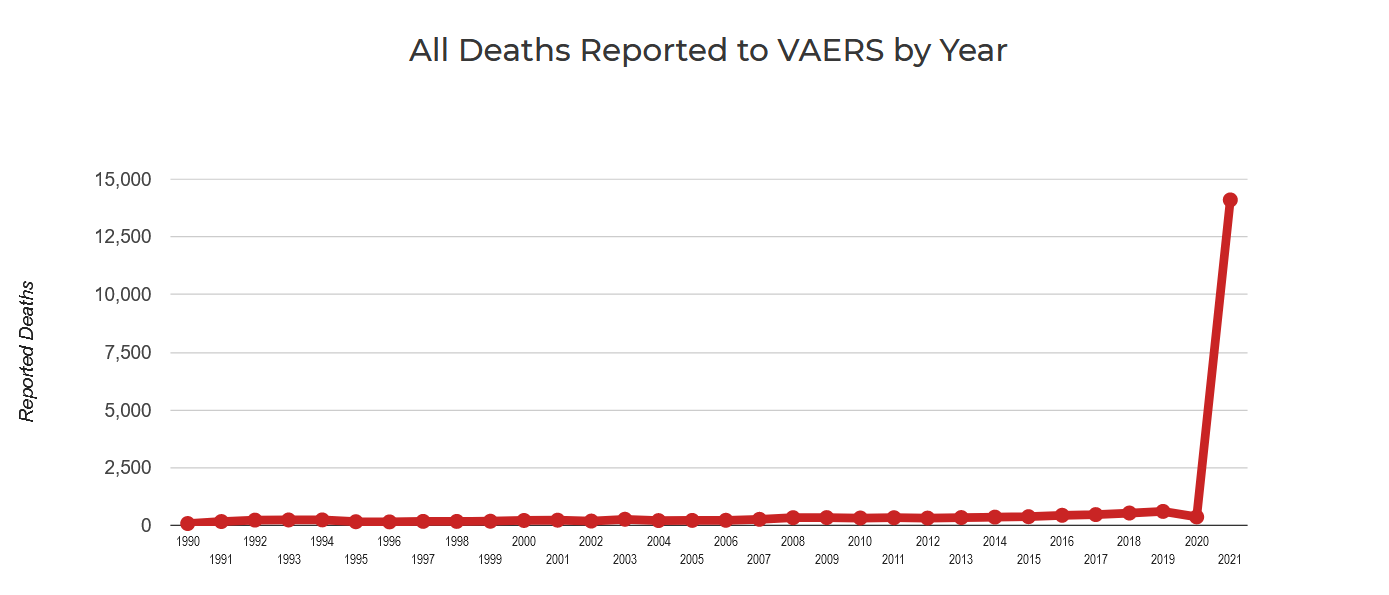
Latest updates
Basics
General
- The Covid Vaccine War (December 2021)
- The Return of the Flu (November 2021)
- The WEF and the Pandemic (October 2021)
- Global Covid Mortality (September 2021)
- Variants: What’s next? (July 2021)
- Obesity and the pandemic (June 2021)
- The failure of PCR mass testing (June 2021)
- Pre-symptomatic transmission (June 2021)
- Covid versus the flu, revisited (March 2021)
- Lockdowns in China in 2021 (February 2021)
- Why Covid-19 is a “strange pandemic” (Sept. 2020)
Vaccines
- Covid Vaccines: A Reality Check (December 2021)
- Covid vaccine adverse events (December 2021)
- Israel: Highest infection rate in the world (Sept. 2021)
- Israel: Why is all-cause mortality increasing? (April 2021)
- Videos: Vaccines: Successes and Controversies (Dec. 2020)
Early Treatment
- The Ivermectin Debate (July 2021)
- Covid and anti-androgens (July 2021)
- Molnupiravir: Caution (October 2021)
- Severe covid: An autoimmune attack (July 2021)
- Is budesonide really effective against covid? (April 2021)
- Remdesivir: An Epidemic Failure (October 2020)
Face masks
- The Mask Folly in Retrospect (August 2021)
- Danish Mask Study: No Benefit (November 2020)
- WHO Mask Study Seriously Flawed (September 2020)
Other topics
- Judgment day: Sweden vindicated (Dec. 2021)
- Omicron Hits the Mutation Jackpot (Nov. 2021)
- Meanwhile in Australia (June 2021)
- The Censorship Pandemic (May 2021)
- On the “people collapsing in Wuhan” (April 2021)
- Lockdowns: Fewer Suicides in 2020? (April 2021)
